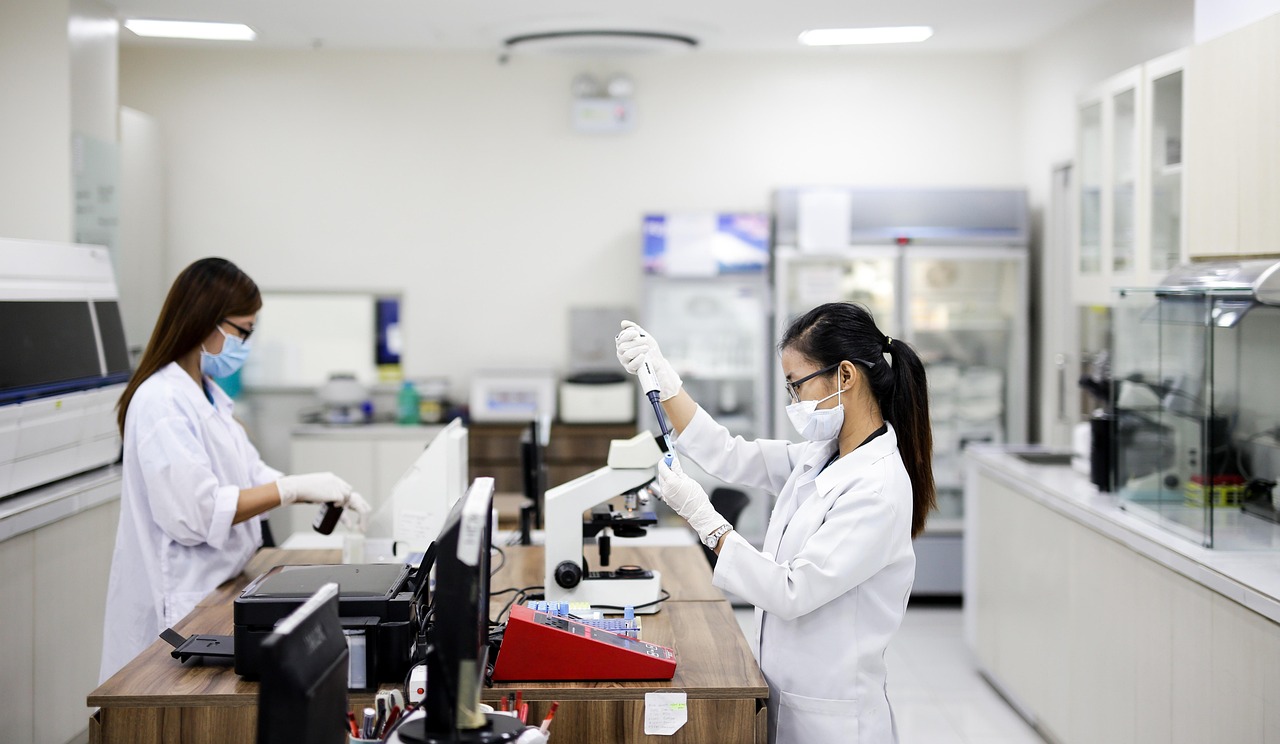
In a recent industry analysis, a medical office technology guide identified eight essential features and five distinct system options that healthcare providers should evaluate when selecting a new telephone solution. The guide, published on a professional telecommunications blog, highlights the growing importance of integrated, secure, and scalable communication platforms in medical practices across the globe.
Key Features for Medical Phone Systems
Healthcare facilities must prioritize phone systems that support advanced call routing, allowing incoming patient inquiries to be directed to the appropriate department or specialist with minimal delay. Integrated voicemail that can be accessed from multiple devices ensures that critical messages are not missed, particularly during after‑hours periods. Compatibility with electronic health record (EHR) software is another crucial feature; it permits the automatic logging of call details, which helps maintain accurate patient histories and facilitates audit trails required by regulatory bodies.
Security and privacy are paramount in medical communications. Systems must adhere to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States and equivalent regulations in other jurisdictions, providing end‑to‑end encryption for voice and data. Mobile integration, whereby staff can answer calls and manage voicemails through smartphones or tablets, offers flexibility for clinicians who travel between patient sites or work remotely. Call analytics, which track metrics such as average handling time and call volume, enable practices to optimize staffing and improve patient satisfaction.
Scalability is a practical consideration; a system that can accommodate a growing number of users without significant infrastructure changes reduces long‑term costs. The overall cost structure, including upfront installation, monthly subscription fees, and any hidden charges for add‑ons, must be transparent so that practices can budget accurately. Finally, reliable customer support and regular software updates are essential for maintaining system integrity, especially when dealing with sensitive health information.
Five System Types for Medical Practices
The guide categorizes phone solutions into five broad types, each with distinct deployment models and feature sets. The first type is a traditional on‑premises Private Branch Exchange (PBX), which requires hardware installation and maintenance but offers complete control over network traffic and data storage. The second type is a hosted PBX, where the provider manages the infrastructure while the practice retains user administration; this model balances control with reduced maintenance overhead.
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) solutions deliver voice communication over broadband networks, often at lower operational costs and with greater flexibility for remote work. Hybrid VoIP systems combine on‑premises hardware with cloud services, allowing practices to maintain critical functions locally while taking advantage of cloud scalability for additional features such as call analytics and integration with patient portals.
Finally, fully cloud‑based contact center platforms provide a comprehensive suite of tools, including automated call routing, interactive voice response (IVR), and real‑time monitoring dashboards. These platforms are designed for high‑volume environments, such as large medical groups or hospital outpatient departments, and typically offer subscription pricing based on the number of active users and the level of service required.
Implications for Healthcare Providers
Adopting a modern phone system can streamline patient communication, reduce administrative burden, and enhance compliance with privacy regulations. The transition to cloud‑based or hybrid models is especially significant for practices that need to support telehealth services, as these systems can integrate with video conferencing tools and electronic appointment scheduling platforms.
While the guide does not endorse any particular vendor, it emphasizes that healthcare providers should conduct thorough evaluations of each system type against their specific operational requirements. Key criteria include security certifications, interoperability with existing EHR systems, and the ability to support mobile devices used by clinicians on the move.
Future Outlook
Industry experts predict that the demand for integrated, secure communication solutions in medicine will continue to rise as telehealth expands and regulatory scrutiny intensifies. Healthcare providers are expected to adopt systems that offer robust analytics and easy scalability, ensuring they can respond to changing patient volumes without compromising data security. As the technology landscape evolves, new features such as artificial intelligence–driven call routing and predictive analytics may further transform how medical offices manage patient interactions.